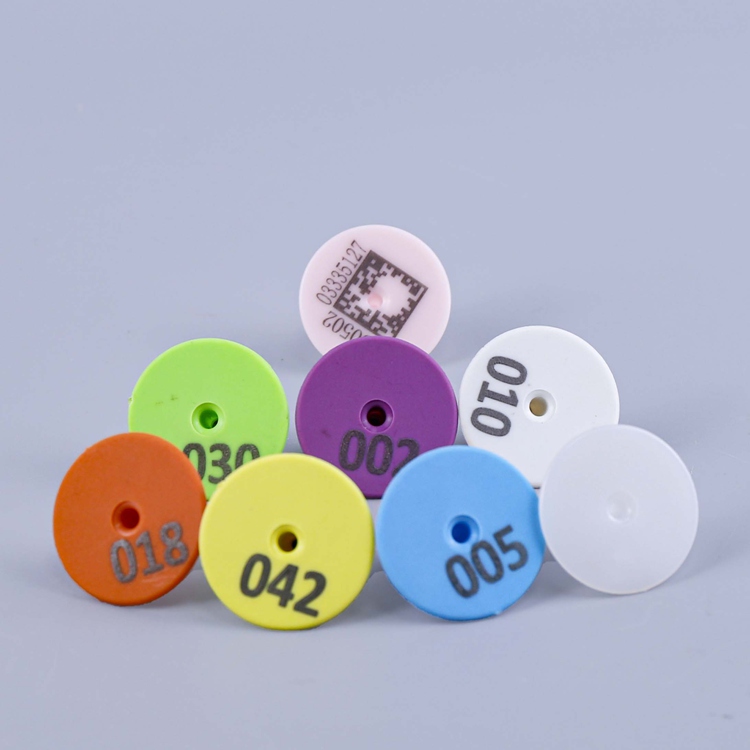
Electronic Ear Tag Animal Ear Tag
1、 Product Overview: Electronic Ear Tag is an intelligent animal identification tool based on Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) or Internet of Things technology, which assigns practical and innovative electronic identification to each animal by fixing...
1、 Product Overview
Electronic ear tag is an intelligent animal identification tool based on radio frequency identification (RFID) or Internet of Things technology, which assigns practical and innovative electronic identification to each animal by fixing it on their ear. Its core function is to achieve personalized information management, behavior monitoring, and full lifecycle data tracking, widely used in animal husbandry, pet management, animal protection, and research industries. Compared to traditional visual signage such as ear tags and tattoos, electronic ear tags have advantages such as large information capacity, good recognition accuracy, and good resistance to environmental interference, making them an important infrastructure for modern animal management.
2、 Core functions and technical principles
Realistic and innovative identity identification
Each electronic ear tag is equipped with a microchip that stores practical and innovative digital codes (usually 15-24 digits), which are bound to animal basic information (such as breed, gender, date of birth) and dynamic data (such as immunization records, growth cycle). The chip adopts a universal protocol, confirms cross system compatibility, and supports data sharing and traceability within the scope.
Non contact data collection
By using a matching reader/writer device, ear tag information can be read contactless within a range of 1-10 meters (depending on the frequency band) to avoid stress reactions caused by manually capturing animals. Low frequency ear tags (134.2kHz) have strong penetration and are suitable for metal dense environments; High frequency (13.56MHz) and higher frequency (860-960MHz) ear tags have suitable reading speeds, support simultaneous recognition of multiple tags, and are suitable for scenarios such as automated grouping and channel counting.
Health and behavior monitoring (optional)
Some excellent models integrate temperature sensors, accelerometers, or GPS modules, which can monitor animal body temperature, activity level, and location information in real time. The data is wirelessly transmitted to the cloud platform to assist breeding personnel in timely detecting actual symptoms of illness (such as fever, reduced activity) or abnormal behavior (such as isolation, wandering), and improve the level of disease prevention and welfare management.
Full chain traceability management
Combined with the aquaculture management system, electronic ear tags can record the entire process data of animals from birth, feeding, transfer, transportation to slaughter, forming an immutable electronic file. In the food safety industry, consumers can enhance trust by scanning the product QR code to inquire about the source of animals, breeding environment, and quarantine certificates.
3、 Product type and applicable scenarios
Classified by frequency band
Low frequency electronic ear tags: Low cost, good resistance to metal interference, commonly used for individual identification and asset management of large livestock such as cattle and sheep.
High frequency/high frequency electronic ear tags: with long reading distance and high speed, suitable for automated management of large-scale pig farms and poultry farms, such as intelligent feeding and group door control.
Dual frequency electronic ear tag: integrating low-frequency and high-frequency technologies, balancing penetration and reading efficiency, suitable for meticulous management in complex environments.
Classified by Form
Ear buckle ear tag: fixed to animal ears through plastic buckles, easy to install, cost-effective, and is the mainstream choice in animal husbandry.
Injectable glass tube ear tag: The microchip is encapsulated in a biocompatible glass tube and implanted subcutaneously into animals through a syringe. It has strong concealment and is suitable for pets, laboratory animals, or high-value livestock.
Collar style electronic identification: Integrated ear tag function and positioning module, suitable for grazing scenes or animal tracking, but requires regular battery replacement.
Classified by functional extensions
Basic ear tags: only support identity recognition and basic data storage, meeting basic management needs.
Intelligent Ear Tag: Equipped with built-in sensors and low-power Bluetooth/LoRa modules, it can actively upload health data to mobile phones or computers to assist in optimizing aquaculture.
4、 Product advantages
Improve management efficiency
Electronic ear tags replace traditional manual recording, achieving automated data collection and synchronization, reducing manual errors and labor intensity. For example, in large-scale pig farms, the system can automatically calculate the feed intake and weight gain rate of each pig, providing a basis for adjusting feeding in multiple regions.
Enhance biological safety
By monitoring animal activity and health data in real-time, breeders can quickly and appropriately isolate suspected infected individuals and block the transmission path of the disease. Meanwhile, electronic ear tags support the electronicization of epidemic prevention information, avoiding the risk of paper records being lost or tampered with.
Optimize resource allocation
Combining big data analysis, electronic ear tags can help farms identify high-yield individuals and optimize breeding strategies for livestock; Or dynamically adjust the feeding plan based on the animal's growth stage to reduce feed waste and breeding costs.
In line with industry trends
With the increasing public attention to food safety and animal welfare, electronic ear tags have become a standard tool for intelligent farming. Its data traceability meets the purchasing standards of markets such as the European Union and the United States, helping agricultural product export enterprises enhance their competitiveness.
5、 Precautions for use
Installation specifications
Choose the avascular area in the middle of the animal's ear to fix the ear tag, avoiding tissue damage or infection.
Injectable ear tags need to be operated by dedicated personnel to confirm that the chip implantation scale and angle meet the requirements.
environmental adaptability
The ear tag shell should have waterproof (based on actual reports), dustproof, and UV resistant capabilities, and be suitable for outdoor high temperature, humid, or cold environments.
Regularly check the fixation status of ear tags to prevent them from falling off due to animal bites or friction.
Data security
Using encryption technology to protect sensitive information stored in ear tags, preventing unauthorized reading or tampering.
Cloud platforms need to have data backup and recovery functions to avoid information loss caused by device failures.
Maintenance and replacement
The service life of basic ear tags is usually 5-8 years, while intelligent ear tags need to be replaced regularly based on battery capacity (usually 2-3 years).
When cleaning the surface stains of ear tags, avoid using corrosive chemicals to prevent damage to the chip or antenna.